如何读源码 最近花了一段时间研究了React的源码,收获良多,特此记录。
必须熟知基础知识,也就是说你必须要用过该框架。
熟读相关文档。
大体上了解该框架的功能,特性。
React框架我一直使用,相关文档也熟读。熟读文档的好处是你可以在读源码的过程中,验证各种特性和功能,加深你的理解。前提了解了,那具体的操作步骤呢?
首先在网上找了一些React源码相关的文章读一读。有疑惑的话记录下来,在之后的读源码过程中反问自己。并且把写的好文章保存下来。等自己读过源码后,再做对比。
写一个最简单的Demo。
本地build。前端框架的话在html中引入umd bundle(development build),未压缩的。然后基于上面的Demo进行调试。具体如何操作步骤可自行Google。
理清目录结构。
以上的步骤是我根据这篇文章 记录下来的,大家可自行看这篇文章,文章写的极其好。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import React, { Component } from 'react' ;import ReactDOM from 'react-dom' ;import './App.css' ;class Article extends Component { constructor (props ) { super (props); this .state = { likes: Math .ceil(Math .random() * 100 ) }; } render() { <li> <button onClick={e =>this .like()}> {likes} <b>❤️</b> </ button> <a href={url}>{name}</a> </ li>} } class App extends Component { constructor ( super (); } render() { return ( <div className="App" > <p className="App-intro" > The list of articles is as follows, Please click favorites and likes. </p> <ul> {this.props.articles.map(article => { return <Article name={article.name} url={article.url} / > } )} </ul> </ div> ); } } const articles = [ { name: "输入框的一些知识" , url: "https://chengwen-zheng.github.io/2020/04/29/%E8%BE%93%E5%85%A5%E6%A1%86%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%80%E4%BA%9B%E7%9F%A5%E8%AF%86/" }, { name: "数据库初涉" , url: "https://chengwen-zheng.github.io/2020/04/26/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93%E5%88%9D%E6%B6%89/" }, { name: "redux源码解析" , url: "https://chengwen-zheng.github.io/2020/04/26/redux%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90/" } ]; ReactDOM.render(<App articles = {articles}/>, document .getElementById('root' ));
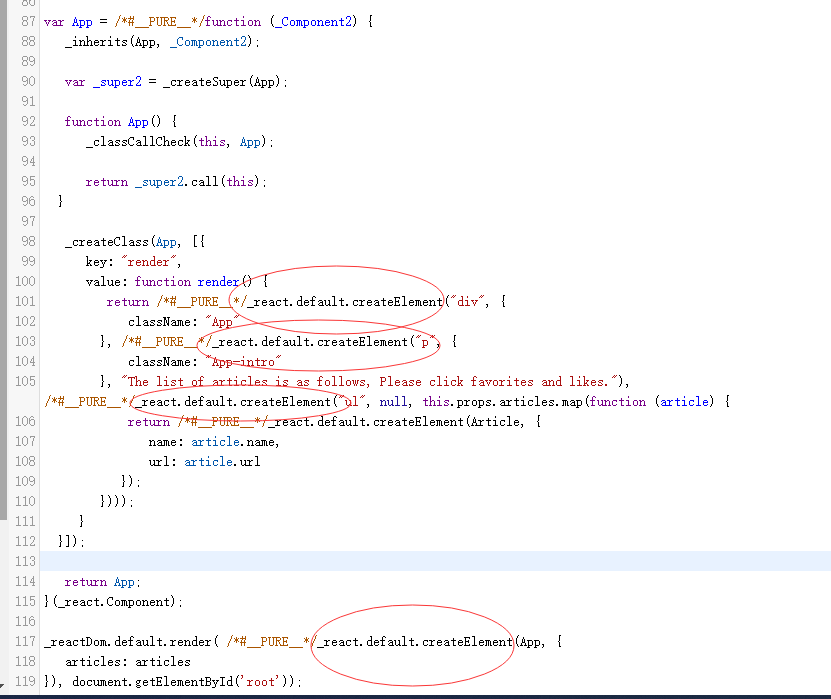
明确React入口以及jsx React代码经过Babel的编译转换,才可以在浏览器中使用。所以我们将该代码用Babel线上转换工具 进行转换,得到如图所示代码。
由图可知,React代码入口为_reactDom.default.render。并且组件变成了一个层层调用_react.default.createElement的函数,也就是我们经常说的编译jsx。那么这个函数究竟做了什么?找到该源码的位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 export function createElement (type , config, children let propName; const props = {}; let key = null ; let ref = null ; let self = null ; let source = null ; if (config != null ) { if (hasValidRef(config)) { ref = config.ref; } if (hasValidKey(config)) { key = '' + config.key; } self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self; source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source; for (propName in config) { if ( hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName) ) { props[propName] = config[propName]; } } } const childrenLength = arguments .length - 2 ; if (childrenLength === 1 ) { props.children = children; } else if (childrenLength > 1 ) { const childArray = Array (childrenLength); for (let i = 0 ; i < childrenLength; i++) { childArray[i] = arguments [i + 2 ]; } } if (type && type .defaultProps) { const defaultProps = type .defaultProps; for (propName in defaultProps) { if (props[propName] === undefined ) { props[propName] = defaultProps[propName]; } } } return ReactElement( type , key, ref, self, source, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props, ); }
可以看出React将所有jsx(也包括Dom元素)变成ReactElement。我们看看ReactElement源码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 const ReactElement = function (type , key, ref, self, source, owner, props const element = { $$typeof : REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, type : type , key: key, ref: ref, props: props, _owner: owner, }; return element; };
ReactElement元素就很简单,是一个有$$typeof、type、key、ref、props属性的对象。
ReactDom.render ReactDom利用render函数将ReactElement元素挂载在Dom元素上,也就是说React将渲染以及和Dom相关的工作抽出来交给了ReactDom、ReactNative等。这种分离也达到了跨终端渲染的效果。我们接下来看看ReactDom.render的源代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 const ReactDOM: Object = { createPortal, render( element: React$Element<any >, container: DOMContainer, callback: ?Function , ) { return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer( null , element, container, false , callback ); } };
legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer函数的本质上初始化Container,往后面看。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer ( parentComponent: ?React$Component<any , any >, children: ReactNodeList, container: DOMContainer, forceHydrate: boolean , callback: ?Function , invariant( isValidContainer(container), 'Target container is not a DOM element.' , ); let root: Root = (container._reactRootContainer: any ); if (!root) { root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer( container, forceHydrate, ); if (typeof callback === 'function' ) { const originalCallback = callback; callback = function ( const instance = DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot); originalCallback.call(instance); }; } DOMRenderer.unbatchedUpdates(() => if (parentComponent != null ) { root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer( parentComponent, children, callback, ); } else { root.render(children, callback); } }); } else { if (typeof callback === 'function' ) { const originalCallback = callback; callback = function ( const instance = DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot); originalCallback.call(instance); }; } if (parentComponent != null ) { root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer( parentComponent, children, callback, ); } else { root.render(children, callback); } } return DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot); }
因为是第一次更新,所以Root为null,进入Initial mount。首先向container(也就是document.getElementById(‘root’))挂载_reactRootContainer。进入legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer,legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer的作用是创建ReactRoot。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer ( container: DOMContainer, forceHydrate: boolean , Root const shouldHydrate = forceHydrate || shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container); if (!shouldHydrate) { let warned = false ; let rootSibling; while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) { container.removeChild(rootSibling); } } const isConcurrent = false ; return new ReactRoot(container, isConcurrent, shouldHydrate); } function ReactRoot ( container: Container, isConcurrent: boolean , hydrate: boolean , const root = DOMRenderer.createContainer(container, isConcurrent, hydrate); this ._internalRoot = root; }
可以看出ReactRoot最终创建了Container。挂载在_internalRoot。并且ReactRoot原型链上有render、unmount、legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer、createBatch方法legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer方法最终调用了root.render(children, callback)方法。root就是ReactRoot。所以就是调用了ReactRoot原型链上的render方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 ReactRoot.prototype.render = function ( children: ReactNodeList, callback: ?() => mixed, Work const root = this ._internalRoot; const work = new ReactWork(); callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback; if (callback !== null ) { work.then(callback); } DOMRenderer.updateContainer(children, root, null , work._onCommit); return work; }; function updateContainer ( element: ReactNodeList, container: OpaqueRoot, parentComponent: ?React$Component<any , any >, callback: ?Function , ExpirationTime const current = container.current; const currentTime = requestCurrentTime(); const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, current); return updateContainerAtExpirationTime( element, container, parentComponent, expirationTime, callback, ); } export function updateContainerAtExpirationTime ( element: ReactNodeList, container: OpaqueRoot, parentComponent: ?React$Component<any , any >, expirationTime: ExpirationTime, callback: ?Function , const current = container.current; const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent); if (container.context === null ) { container.context = context; } else { container.pendingContext = context; } return scheduleRootUpdate(current, element, expirationTime, callback); } function scheduleRootUpdate ( current: Fiber, element: ReactNodeList, expirationTime: ExpirationTime, callback: ?Function , const update = createUpdate(expirationTime); update.payload = {element}; callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback; if (callback !== null ) { warningWithoutStack( typeof callback === 'function' , 'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' + 'function. Instead received: %s.' , callback, ); update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(current, update); scheduleWork(current, expirationTime); return expirationTime; }
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer创建了Container,后续更新操作在ReactRoot.render里面进行。在创建的过程中,计算出后续任务调度的优先级,方便以后调度。还有生成update,并更新updateQueue。scheduleWork是开始进行异步任务调度。